Disponible con una licencia de Spatial Analyst.
Resumen
Raises the cell values in a raster to the power of the values found in another raster.
Ilustración
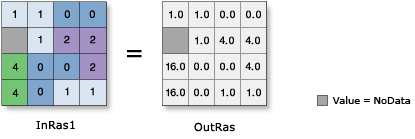
Debate
Cuando se utiliza un operador con una entrada ráster, el resultado será un ráster. Sin embargo, si todas las entradas son números, entonces el resultado es un número.
Cuando se utilizan varios operadores en una expresión, no necesariamente se ejecutan en orden de izquierda a derecha. El operador con el valor de jerarquía más alta se ejecutará primero. Para obtener más información sobre la jerarquía del operador, consulte la tabla jerarquía del operador. Puede utilizar paréntesis para controlar el orden de ejecución.
Output values are always floating point, regardless of the input value type.
Another way to perform the power operation is a **= b, which is an alternative way to write a = a ** b.
Sintaxis
in_raster_or_constant1 ** in_raster_or_constant2
| Operando | Explicación | Tipo de datos |
in_raster_or_constant1 | The input values to be raised to the power defined by the second input. If the first input is a raster and the second is a scalar, an output raster is created with each input raster value being raised to the power of the scalar value. | Raster Layer | Constant |
in_raster_or_constant2 | The input that determines the power to which the values in the first input will be raised. If the first input is a scalar and the second is a raster, an output raster is created with the scalar value being raised to the power of each input raster value. | Raster Layer | Constant |
Valor de retorno
| Nombre | Explicación | Tipo de datos |
| out_raster | El objeto ráster de salida. The cell values are the result of raising the values in the first input to the power of the values in the second input. | Raster |
Muestra de código
This sample uses the values in the second input raster as the power by which to raise the values in the first input raster.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outPower = Raster("degs") ** Raster("cost")
outPower.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outpower.img")This sample uses the values in the second input raster as the power by which to raise the values in the first input raster.
# Name: Op_Power_Ex_02.py
# Description: Raises the cells in a raster to the power of the values
# found in another raster
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster1 = Raster("degs")
inRaster2 = Raster("cost")
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute Power
outPower = inRaster1 ** inRaster2
# Save the output
outPower.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outpower")